
Is Swallowing Gum Dangerous?
Most of us have been warned at some point: “Don’t swallow your gum—it’ll stay in your stomach for seven years!” It’s a phrase passed around in classrooms, at dinner tables, and even on playgrounds.The idea sounds just plausible enough to make you nervous—but is there any truth to it?
Does gum really sit in your stomach for seven years, or is that just another old wives’ tale designed to scare kids into good manners? Let’s take a closer look at what actually happens when you swallow chewing gum—and what science really says about it.
What Happens When You Swallow Gum?
To understand this, it helps to first think about how your digestive system works with regular food.
When you eat, your body breaks food down using mechanical digestion (chewing and stomach churning) and chemical digestion (stomach acid and digestive enzymes). Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are reduced to smaller molecules that your intestines can absorb into your bloodstream. Whatever your body can’t use—like certain fibers—is excreted as waste.
Chewing gum, however, is a bit of a biological oddball.
Why Gum Doesn’t Digest Like Food
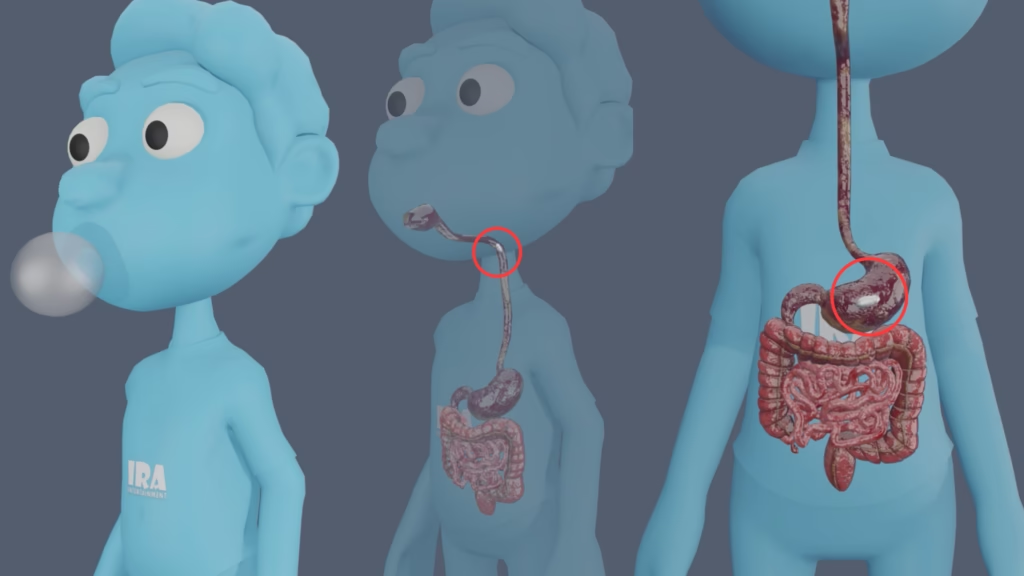
The main reason gum behaves differently is its gum base—the chewy, rubbery part that makes gum flexible and stretchable. Modern gum bases are made of a combination of synthetic resins, elastomers, and waxes. These materials are resistant to the body’s digestive enzymes and stomach acid.
Here’s what happens step by step:
You swallow gum (intentionally or accidentally).
The sweeteners, flavorings, and softeners dissolve and are digested just like food.
The gum base remains intact—it doesn’t dissolve or get broken down.
Your digestive system moves it along through the intestines using peristalsis (muscle contractions that push food along).
Within a few days, the gum base exits your body naturally, just like other indigestible materials—such as corn skins or small seeds.
In short, while gum doesn’t break down in your stomach, it also doesn’t “stick” around for years. Your digestive system is well-designed to keep things moving.
The 7-Year Myth

The “seven years in your stomach” myth is one of those stories that has been passed down for generations, but no one quite knows where it started. There’s no scientific basis for it whatsoever.
So why did it spread so widely?
The most likely explanation is behavioral parenting. Adults likely wanted to discourage kids from swallowing gum, so they came up with a scary—but harmless—story to stop the habit. It’s similar to other popular childhood myths, like:
“If you cross your eyes, they’ll get stuck that way.”
“If you swallow watermelon seeds, a plant will grow in your stomach.”
“Cracking your knuckles causes arthritis.”
While these sayings are catchy, none of them hold up under scientific scrutiny. The “gum in your stomach for seven years” myth simply stuck (pun intended) because it’s memorable.
What’s Really Inside Chewing Gum?

Modern chewing gum is a carefully engineered product. Although the recipes differ between brands, most gum contains a similar combination of components:
| Ingredient | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Gum base | Provides the chewy, elastic texture. Made of elastomers (rubbery materials), resins, and waxes. |
| Sweeteners | Add flavor. Can be sugar or sugar substitutes like xylitol, sorbitol, or aspartame. |
| Flavorings | Mint, fruit, cinnamon, or other extracts for taste. |
| Softeners | Ingredients like glycerin or vegetable oil to prevent gum from hardening. |
| Colorants | Give the gum its color (natural or artificial dyes). |
Everything except the gum base is digestible. That’s why your body can absorb the flavoring and sweeteners but not the chewy part itself.
Interestingly, gum composition has changed over time. Early gum was made from natural chicle, a latex sap from the sapodilla tree, while modern versions often use synthetic rubber bases (like butadiene-styrene) for consistency and shelf life.
What Doctors and Scientists Say
Medical professionals have long known that swallowing gum occasionally poses little to no health risk. According to the Mayo Clinic and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), gum passes harmlessly through the digestive system in most cases.
However, there are rare exceptions where swallowing gum—especially repeatedly—can cause problems.
Rare But Real Risks of Swallowing Gum

1. Gastrointestinal Blockages (Bezoars)
If someone swallows large amounts of gum—or gum combined with other indigestible items (like sunflower seed shells or coins)—it can form a bezoar. A bezoar is a mass that can’t easily pass through the intestines and may lead to intestinal obstruction.
While this sounds alarming, it’s extremely rare. Most reported cases involve young children who swallowed several pieces of gum in a short period, sometimes along with other materials.
Symptoms of an intestinal blockage include:
Abdominal pain
Constipation
Vomiting
Bloating
Loss of appetite
If these occur after frequent gum swallowing, a doctor may need to evaluate the digestive tract using imaging techniques like X-rays.
2. Children Are More Vulnerable
Children’s digestive tracts are smaller, which means blockages can occur more easily. Moreover, children are more likely to swallow gum unintentionally—or even intentionally—out of curiosity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics documented cases in the 1990s of children who developed constipation or intestinal blockages after swallowing multiple pieces of gum daily. In these rare situations, the gum combined with stool to form a large, hard mass that was difficult to pass.
That’s why pediatricians often advise teaching children early on that gum is for chewing, not swallowing.
3. Constipation and Stool Impaction
Frequent gum swallowing can contribute to constipation, especially if combined with low-fiber diets or dehydration. In some cases, swallowed gum acts like glue, helping stool and indigestible materials stick together and harden.
Fortunately, these issues can usually be prevented with:
Plenty of hydration
A fiber-rich diet (fruits, vegetables, and whole grains)
Limiting gum swallowing altogether
4. Choking Hazards
The biggest immediate risk of gum swallowing—particularly for young children—is choking. Because gum is slippery and pliable, it can accidentally block the airway if inhaled or swallowed the wrong way.
That’s why pediatricians recommend that children under age 5 not chew gum at all. For older kids, adult supervision and good habits (no running or laughing while chewing) can prevent accidents.
Does the Type of Gum Matter?
You might wonder whether sugar-free gums, natural gums, or traditional gums behave differently when swallowed. The short answer: not really.
Sugar-free gum often uses synthetic bases like polyisobutylene and the same types of resins found in regular gum.
Natural gums (like chicle or mastic gum) are made from tree sap and are still indigestible by human enzymes.
Bubble gum, despite being softer and stickier, also uses similar bases and passes through the body the same way.
So regardless of the brand or formulation, your digestive system will treat the gum base as non-digestible material and move it along naturally.
The Role of Peristalsis: Your Body’s Conveyor Belt
The reason gum doesn’t linger in your stomach isn’t magic—it’s biology.
Your digestive tract uses a process called peristalsis, which involves rhythmic muscle contractions that push food (and non-food) items through your gastrointestinal tract. Even materials that can’t be digested—like small bits of plastic, hair, or gum—will usually pass through in 24 to 72 hours.
This means that gum doesn’t “stick” anywhere along the way. Your stomach and intestines are coated with mucus that prevents most substances from adhering to the walls. Instead, the gum base simply travels the same route as everything else, until it exits the body.
What About People With Digestive Disorders?
For people with normal digestion, swallowed gum is harmless. However, individuals with certain digestive disorders—like Crohn’s disease, intestinal strictures, or motility disorders—may want to be more cautious.
Because their intestines might already have narrowed sections or slower movement, indigestible materials (including gum) could theoretically contribute to a blockage. For these patients, doctors often recommend avoiding swallowing gum entirely.
Is Gum Actually Good for You? (Surprising Benefits)
While swallowing gum isn’t beneficial, chewing gum can actually have several health benefits when used correctly.
1. Improves Oral Health
Sugar-free gum, especially those sweetened with xylitol, can help prevent cavities. Chewing stimulates saliva production, which neutralizes acids in the mouth and washes away food debris.
2. Aids Digestion (When Not Swallowed)
Chewing increases saliva flow, which can ease acid reflux and indigestion in some people. It also helps your body transition into “digestive mode,” preparing your stomach for food.
3. Boosts Focus and Memory
Several studies have shown that chewing gum can temporarily improve concentration, memory, and alertness, possibly due to increased blood flow to the brain.
4. Helps Curb Cravings
Chewing gum may reduce appetite or prevent mindless snacking, making it a useful tool for weight management when used responsibly.
Fun Fact: Gum in Space!
Even astronauts chew gum! NASA once included gum in space mission kits because chewing helps relieve pressure in the ears and maintain oral hygiene in low-gravity environments. Of course, swallowing gum in space would still be discouraged—because waste management in microgravity is complicated enough!
Common Myths About Swallowing Gum—Debunked
| Myth | Truth |
|---|---|
| “Gum stays in your stomach for seven years.” | False. It passes through your digestive system like other indigestible items. |
| “Swallowing gum can poison you.” | False. The ingredients are safe for chewing and don’t release toxins when swallowed. |
| “Natural gum digests better than artificial gum.” | False. All gum bases resist digestion. |
| “Swallowing gum helps with heartburn.” | Partly false. Chewing gum may help with heartburn—but swallowing it won’t. |
The Takeaway: Should You Worry About Swallowing Gum?
Accidentally swallowing gum once in a while is not dangerous.
Your body can’t digest the gum base, but it will pass it naturally within a few days.
Serious complications like blockages or constipation are extremely rare and typically occur only after frequent or excessive swallowing—especially in children.
The “seven-year myth” is just that—a myth, likely created to discourage bad habits.
So, if you accidentally swallow your gum, don’t panic. Your digestive system knows exactly what to do.
But still—gum is made for chewing, not eating. The safest and healthiest habit is to spit it out into the trash when you’re done.
About the Author
This article was prepared by the IRA Studios editorial team, creators of high-quality 3D educational visualizations designed to simplify complex ideas through clear and engaging visuals.
Watch the Full 3D Animation
To explore all of these processes in 3D, check out our detailed 3D Animation video.
Watch it in Malayalam
Want to learn more through visual storytelling? Check out our detailed 3D explanation blog on What Really Happens When You Hold Your Pee? (3D Explained)